|
|
6 years ago | |
|---|---|---|
| design | 6 years ago | |
| img | 6 years ago | |
| readme_images | 6 years ago | |
| sig-ask-devosan | 6 years ago | |
| CNAME | 6 years ago | |
| README.md | 6 years ago | |
| additionalScripts.js | 6 years ago | |
| index.html | 6 years ago | |
| sig-ask-devOsan.js | 6 years ago | |
| styles.css | 6 years ago | |
README.md
Design Palette
Himalaya (dark brown) #696035
Swamp (less black) #202222
Contributing
Please feel free to update this document. There's probably a bunch of ambiguous directions that I take for granted.
Feel free to ask any questions in the Facebook group or when we meet up at the club.
Create a Github account
Install and get familiar with Git
Follow this guide to install Git https://help.github.com/en/articles/set-up-git. If you're feeling real motivated, that guide will pretty much walk you through everything I'm going to lay out here. Understanding Git is going to be really important. There are ways to work around it, but if you learn it, collaborating on code with others will be much easier. Other than the original website, here is a good starter resource https://www.codecademy.com/learn/learn-git
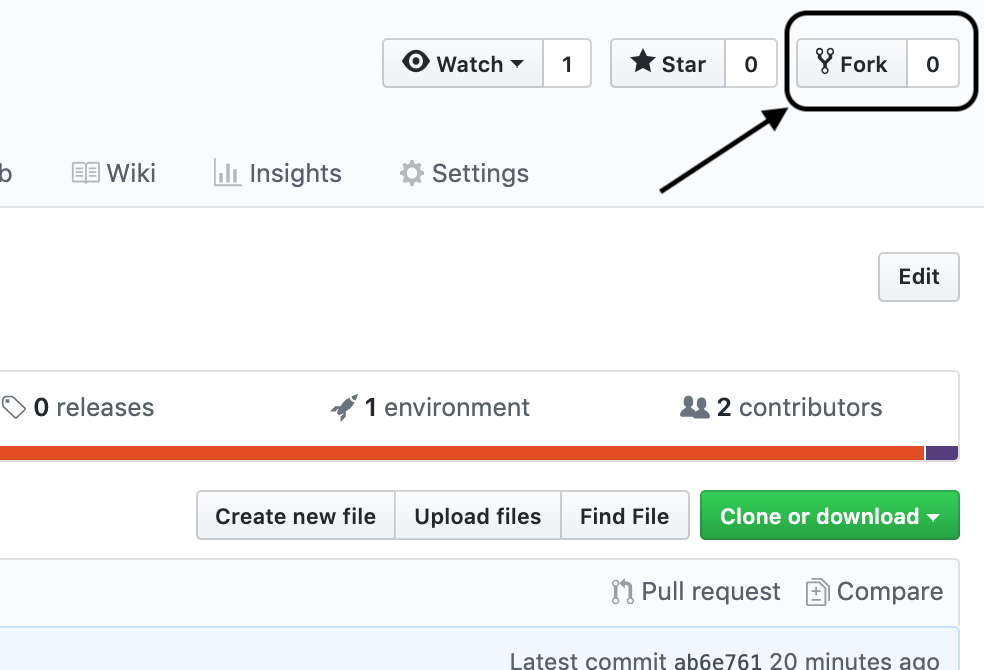
Fork the Repository (repo)
Click on the Fork button at the top right of the page. This will create a copy of the repository in your github account. The copy is linked to the original, so when you make a pull request, it knows where it's going.
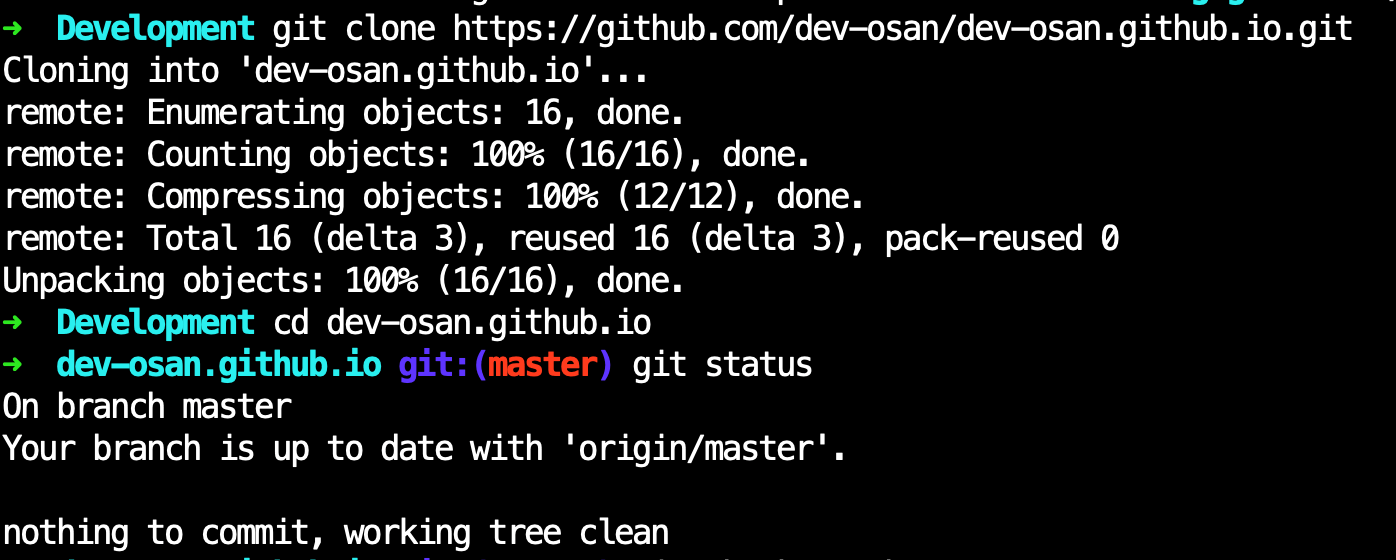
Clone down your new copy of the repository to your computer
Open your terminal or command prompt and navigate to the directory you want to store the code. This is just like navigating the folders on your computer, just that you're doing it from the terminal - none of that fancy graphical user interface (gui) anymore! You can view a list of files and folders by typing ls (mac) or dir (windows) and hitting Enter. You can go into another folder by using the change directory command cd folderName and hitting Enter. You can navigate up a folder by typing cd .. and hitting Enter. Once you are in the folder you want to create the project folder in, click the clone or download button (It's green, top right) and copy the URL that it shows. Once you do that, go back to your terminal and type git clone https://github.com/userName/repoName Make sure to swap out the URL for the one you copied! After it downloads, type cd dev-osan.github.io and hit enter to navigate into the newly created folder. This is where everything was downloaded to.
Let's make sure we're watching the original repository
If someone changes the original repo, you want to make sure you can get those changes to, so in the terminal, type git remote add upstream https://github.com/dev-osan/dev-osan.github.io.git and hit Enter. You can run git fetch upstream to pull down any new changes to the original repo that others may have done. Make sure to do this each time you're about to tackle an issue or make changes to ensure you're working in the most up to date version.
Make changes!
Open your code editor, I use Visual Studio Code, and open the folder that you just created. Once that's done, you should be able to see the files from the project, hopefully with some nice colors (syntax highlighting). Edit the code and save your files!
Commit the changes you've made.
Git works by staging the files you want to commit, and then you have to commit them while providing a message. This is like a big save to the overall codebase. In your terminal, write git add . and hit Enter. This adds all of the changed files to the staging area. Then when you're ready, type in git commit -m 'I promise to write a quick summary of my changes here using future tense language.' and hit Enter.
Now let's push the code back up to github!
After committing all of your changes (you can make multiple commits), it's time to push up the code. Type git push and hit Enter. At this point, if you've never done this before you may need to type in your github login credentials. You can also git push as many times as you like before you go to the next step.
The Pull Request
At this point, you're ready to make a pull request, which is like saying "Hey original repo, will you pull my changes into yours, please?" On your repo page, click New Pull Request and follow the instructions through submitting the pull request. We'll review it, merge it, or give you feedback!
Rinse & Repeat
self explanatory
Resources
This isn't the first time someone has attempted to write a contribution guide. Here are some other guides people have written or places to find more information on git and contributing to open source.
Creating a pull request from a fork
Contributing
First Contributions
GitHub Help and Documentation
How to Keep a Downstream git Repository Current with Upstream Repository Changes
Your first open source contribution: a step-by-step technical guide